How It Works¶
Key concepts¶
- CWL descriptor file - YAML or JSON file to describe the workflow inputs, outputs and steps. File should be compatible with CWL v1.0 specification
- Job file - YAML or JSON file to set the values for the wokrflow inputs.
For cwl-airflow to function properly the Job file should include 3 mandatory and
one optional fields:
- workflow - mandatory field to specify the absolute path to the CWL descriptor file
- output_folder - mandatory field to specify the absolute path to the folder where all the output files should be moved after successful workflow execution
- tmp_folder - optional field to specify the absolute path to the folder for storing intermediate results. After workflow execution this folder will be deleted.
- uid - mandatory field that is used for generating DAG’s unique identifier.
- DAG - directed acyclic graph that describes the workflow structure.
- Jobs folder - folder to keep all Job files scheduled for execution or the ones that have already been processed. The folder’s location is set as jobs parameter of cwl section in Airflow configuration file.
What’s inside¶
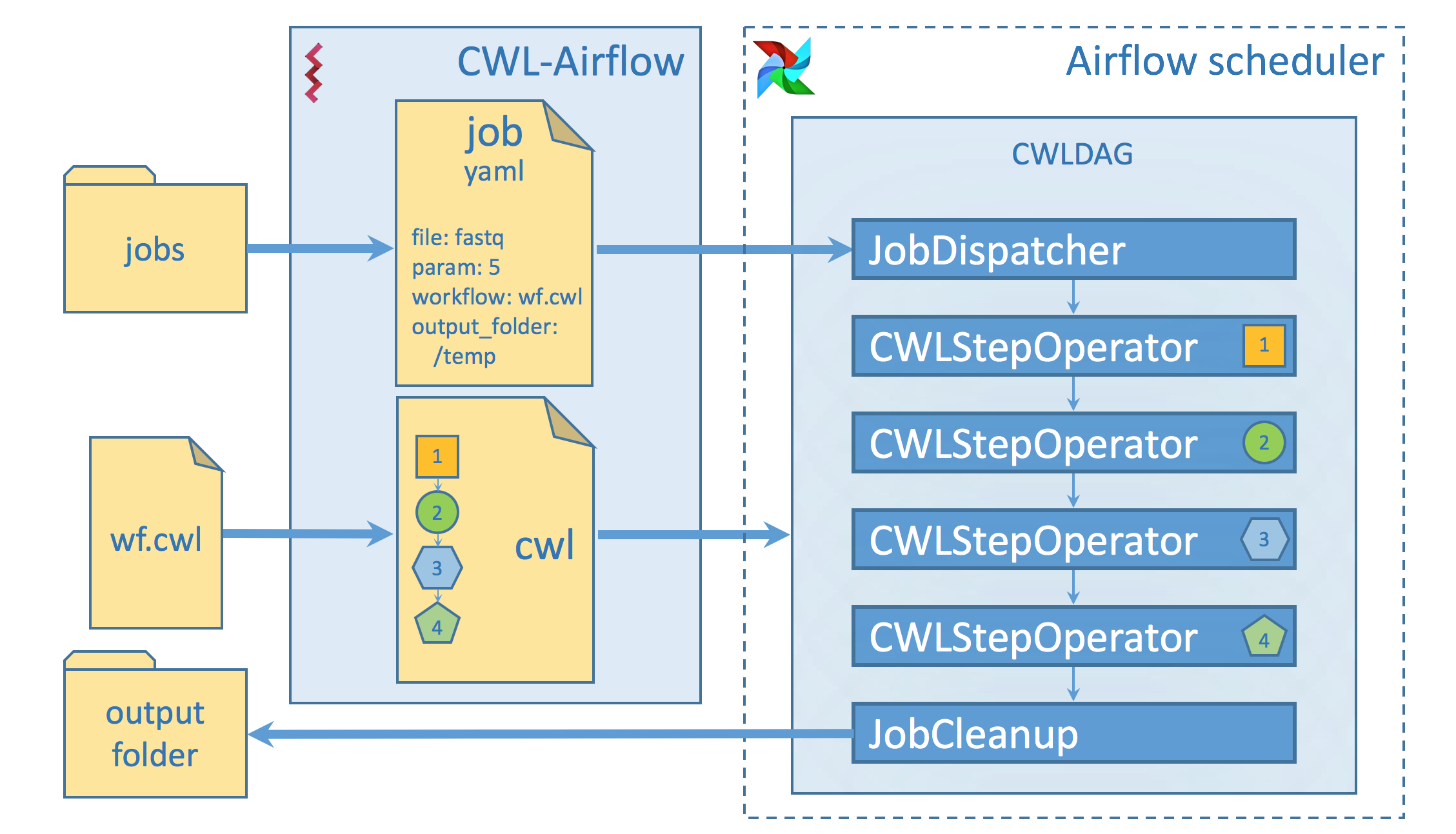
To build a workflow cwl-airflow uses three basic classes:
- CWLStepOperator - executes a separate workflow step
- JobDispatcher - serializes the Job file and provides the worflow with input data
- JobCleanup - returns the calculated results to the output folder
A set of CWLStepOperators, JobDispatcher and JobCleanup are
combined in CWLDAG that defines a graph to reflect the workflow steps, their relationships
and dependencies. Automatically generated cwl_dag.py script is placed in the DAGs folder. When Airflow
Scheduler loads DAGs from the DAGs folder, the cwl_dag.py script parses all the Job files from the Jobs folder
and creates DAGs for each of them. Each DAG has a unique DAG ID that is formed accodring to the following scheme:
CWL descriptor file basename-Job file basename-uid field from the Job file
 CWL-Airflow diagram
CWL-Airflow diagram